What is email spoofing? You might have heard that term before. But what exactly does it mean? Email spoofing is like the online version of telephone spoofing. Except instead of your phone number, it's your email address being spoofed.
A **spoof** can be a verb or noun description. Spoof as a verb means to **deceive** or **make a fake**. Spoof as a noun means **a deception** or **impersonation** for the purpose of tricking someone. Simple definition: To spoof an email makes it look like another message came from an email address other than yours. Another way to explain email spoofing is to change your email address (the FROM field) to look like someone else.
In the world of email, spoofing is used by both spammers and hackers. Spam emails are designed to fool you into clicking on a link in the email message. This can allow malware or phishing attacks onto your computer or smartphone. Spammers also use spoofing to hide their true identity by pretending they are coming from a different email address. Spammers don't just do this for anonymity. Spam networks work together in "networks" to send spam out. Some spammers sell access to these networks (also called spambots or bulk mailers) and allow people who purchase access to use them to send spam. When spammers are spoofing an email address, they usually add a fake return email address so that the person whose name is being used doesn't find out. Spam networks also do this to try and deceive spam blacklists that have real-time updated databases of known spambots.

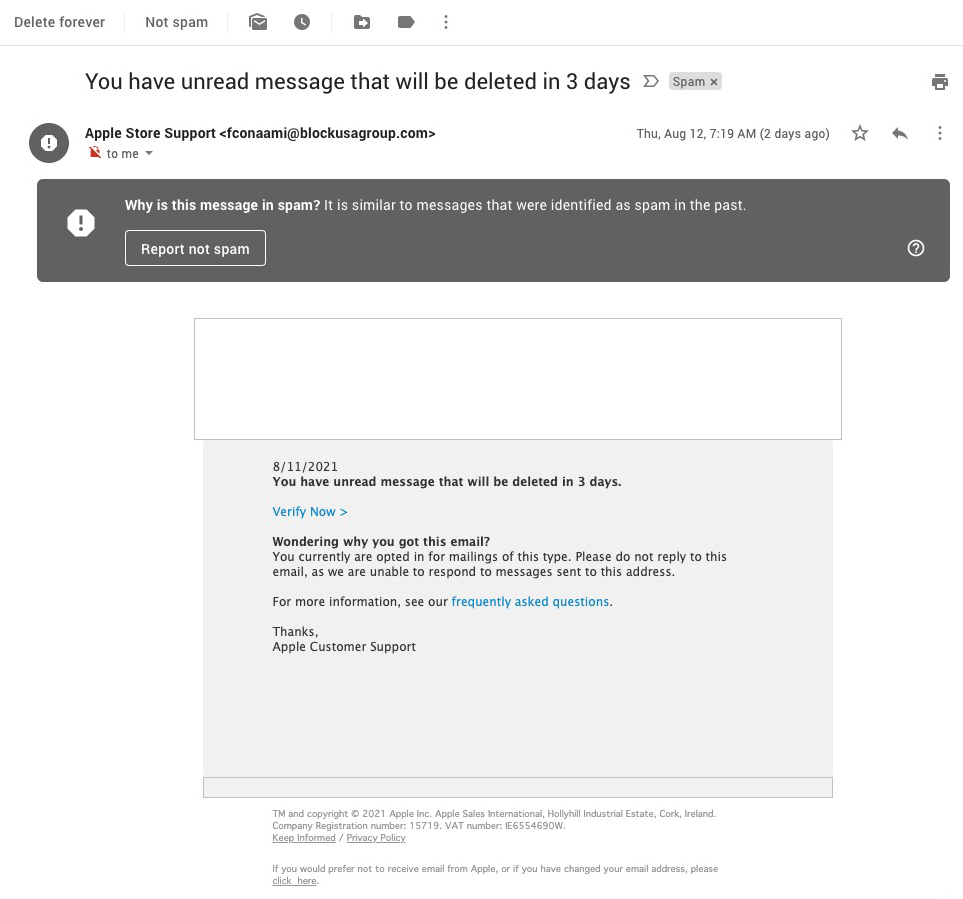
Spammers are still using email spoofing today. This is especially the case if they are sending out their spam via a spambot network. It's much easier for a spammer to get away with an email spoofing campaign when they are using one of these bulk mailers instead of doing everything manually like it was back in the 90s during the early days of spam. Spammers are also using fake email addresses that look like they are coming from a legitimate company. Like the example below where [email protected] is being spoofed to make it look like the message is legitimately coming from Apple instead of some random person or group of people trying to trick you into clicking on a link in their email message. Spammers don't care who's the email address they are using as long as it makes the email more successful in getting people to click on it and possibly infect themselves with some malware or get scammed out of money from a phishing attack. Spam today is being sent by huge networks consisting of thousands or millions of infected computers and smartphones.
You might also hear the term **phishing** which is very closely related to email spoofing. Phishing is quite simply a type of fraud where someone tries to get you to give them your information or login credentials when you think you are dealing with someone trustworthy, like your bank or Apple (for instance).
So if you think you have a hacked account or know someone else whose account has been spoofed and want to report it, read more on what you should do next after being phished. And if you're the victim of spam, check out how to stop getting spammed in my post on how to stop getting spam. Sometimes spammers use techniques other than email spoofing to get people's attention. I was hoping you could read about the different spam-sending techniques here in my post on how spammers try to trick you into clicking their spam messages.
How does spoofing work? Spoofing an email address is easy if you know what your target victim will never check the actual source of where an email came from. Reading the full email headers is not something people do every day, especially if they are using a desktop or webmail client, which by default hides all this information from you.
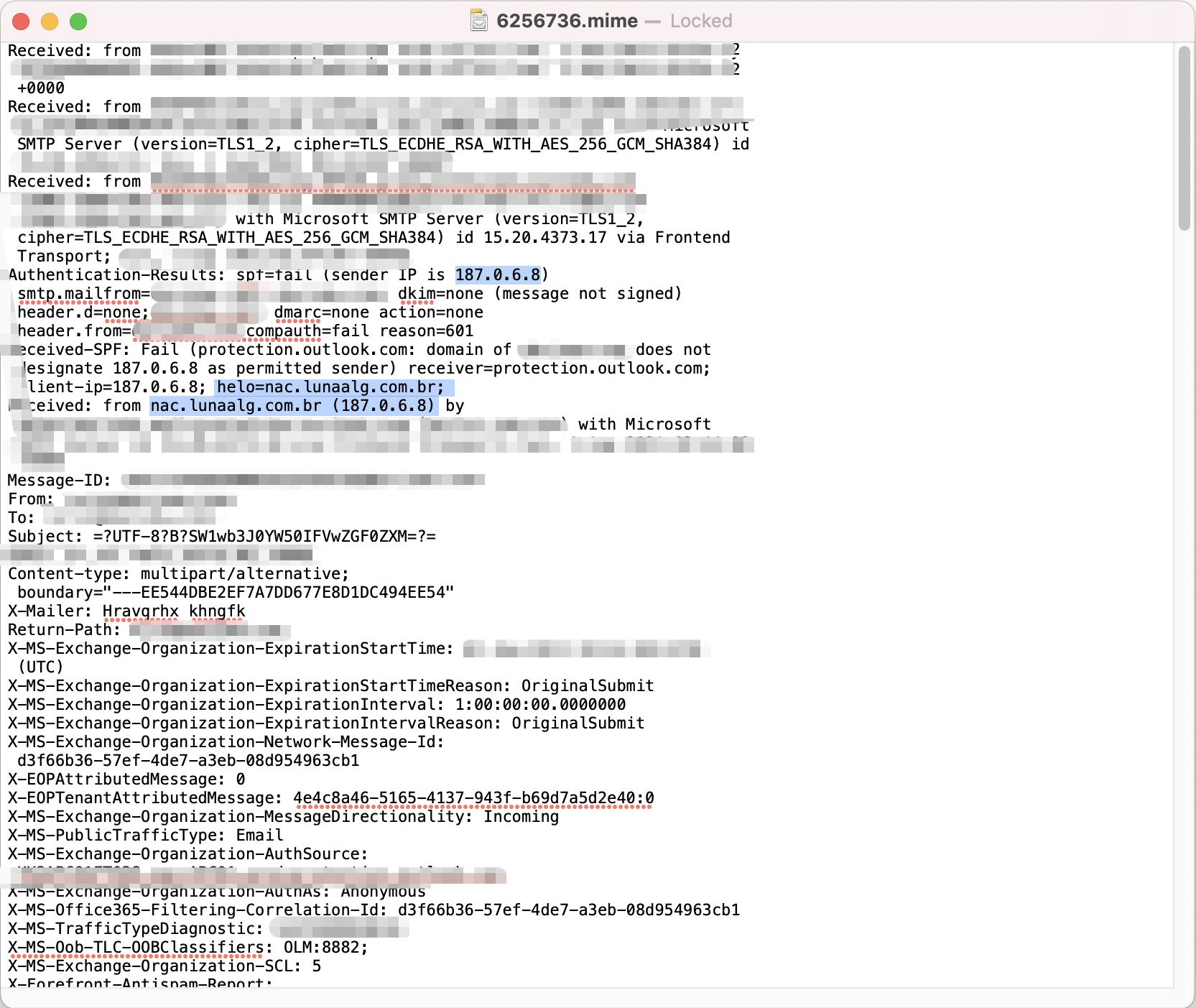
If you are curious to see what an email looks like before you open it (headers and all), if you are using Gmail, you can use "Show Original" to view the header. You can also use the free online tool, Email Header Analyzer. The screenshot below is from a spoofing email that we have received. Spoofed emails usually have the fake return address at the top of the email message in the From line. If you are still having trouble reading it, go ahead and click on the image above to see an enlarged version of this part of the email header. Below is a close-up of the part I'm talking about.
The fake email address is spoofed to look like [email protected], Apple's registered sender name. If you are reading this post and have been a victim of an email spoofing attack, then don't worry because it's not your fault that you've been fooled into opening a spoof email message. It's not your fault because the spammer is trying to deceive you into thinking it's coming from Apple.
The difference between a faked email and a spoofed one is subtle but significant. In the screenshot above, we can see the "Return-Path" field, which is what an email's return path usually looks like. The sentence in this field tells us where the message comes from after being sent from an SMTP server (mail transfer agent). So this sentence is the email address of the person who originally sent it to you; this would have been Apple in the example above.
The word spoofed means that someone has changed the sender name on a message and replaced it with an address that looks different or fake but can control. In other words, you are receiving an email message from a sender that does not exist. So when a spammer is spoofing someone's email address, it means they are using fake information to pretend to be someone else. Spam messages that use this technique usually have no real content because these emails aim to get you to click on whatever link might be embedded in the email message. Spoofing is a tried and tested way to get people to click on links that lead to spam sites hosting malware or to get you to enter your personal details when you think you are logging into your online bank account. If someone spoofed Apple's address, it would be because they wanted you to install a virus or give out your login details etc.
If you have been spoofed, there is a good chance that someone has compromised one of the online services that you use and are trying to get hold of your personal information. But it could also be that they have teamed up with an affiliate who is targeting your niche. And finally, it could just be someone who wants to cause you distress by sending you a spoofed message that looks like it's from Apple. As I mentioned earlier, the goal of this kind of email is to get you to click on something in the email message.
If you think your personal information has been compromised, contact your bank or the service provider and ask that they help reset your login. It is not a good idea to reply to the email with another password request for security reasons.

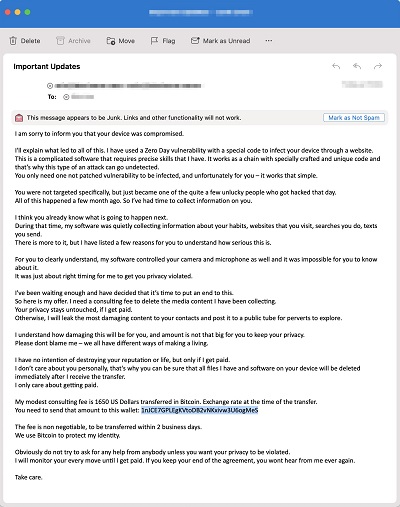
Not all spoof emails are after your personal information, and some want to plant malware or spyware on the victim's computer. For instance, a hacker could have installed something in the victim's device, and by using spoof email, they can monitor their behaviour. They might approach that person out of suspicion for naughty online activity and then threaten them with evidence of said history.
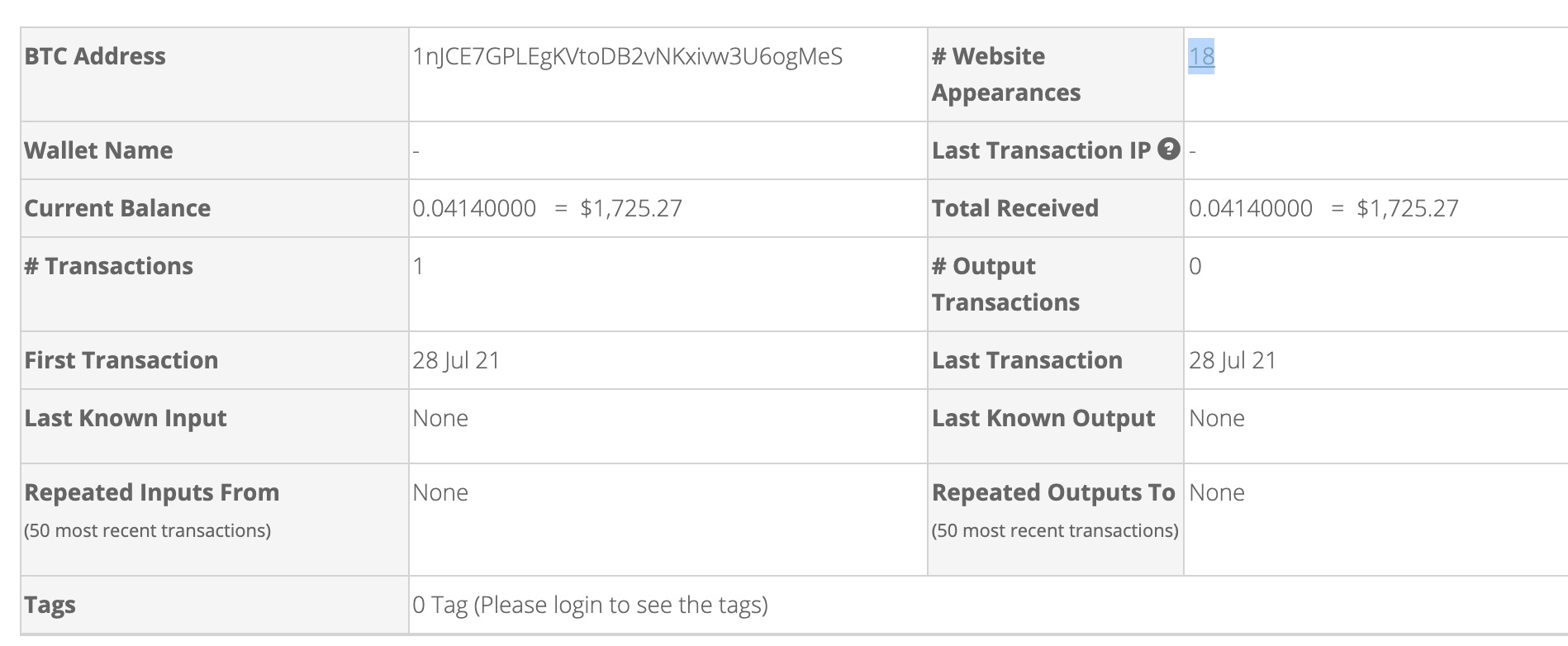
Most of the time, they would want you to pay them with bitcoins so they can avoid leaving any trace of them having hacked into your device or stealing from you. This is called ransoming your device.
So in this article, we've gone over the basic facts about email spoofing. we hope you now have a better idea of what it is and how to protect yourself from being a victim of spoofing attacks. If you want to learn more, you can follow SI Insights as we constantly update the latest Spoof / Phishing emails we received.